Vision-Based Force Estimation for Minimally Invasive Telesurgery Through Contact Detection and Local Stiffness Models
Mar 27, 2024Shuyuan Yang, My H. Le, Kyle R. Golobish, Juan C. Beaver, Zonghe Chua
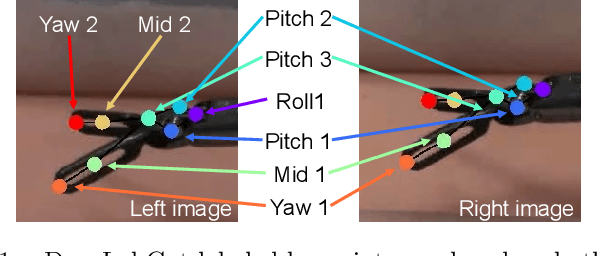

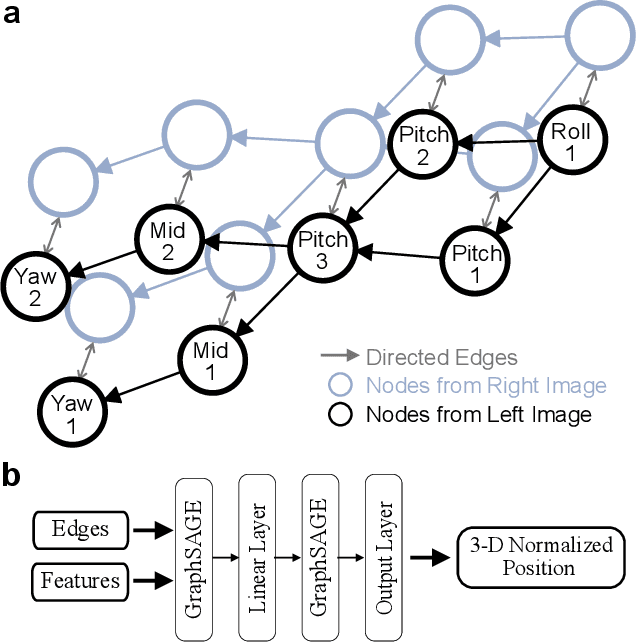

In minimally invasive telesurgery, obtaining accurate force information is difficult due to the complexities of in-vivo end effector force sensing. This constrains development and implementation of haptic feedback and force-based automated performance metrics, respectively. Vision-based force sensing approaches using deep learning are a promising alternative to intrinsic end effector force sensing. However, they have limited ability to generalize to novel scenarios, and require learning on high-quality force sensor training data that can be difficult to obtain. To address these challenges, this paper presents a novel vision-based contact-conditional approach for force estimation in telesurgical environments. Our method leverages supervised learning with human labels and end effector position data to train deep neural networks. Predictions from these trained models are optionally combined with robot joint torque information to estimate forces indirectly from visual data. We benchmark our method against ground truth force sensor data and demonstrate generality by fine-tuning to novel surgical scenarios in a data-efficient manner. Our methods demonstrated greater than 90% accuracy on contact detection and less than 10% force prediction error. These results suggest potential usefulness of contact-conditional force estimation for sensory substitution haptic feedback and tissue handling skill evaluation in clinical settings.
Haptic Guidance and Haptic Error Amplification in a Virtual Surgical Robotic Training Environment
Sep 11, 2023Yousi A. Oquendo, Margaret M. Coad, Sherry M. Wren, Thomas S. Lendvay, Ilana Nisky, Anthony M. Jarc, Allison M. Okamura, Zonghe Chua
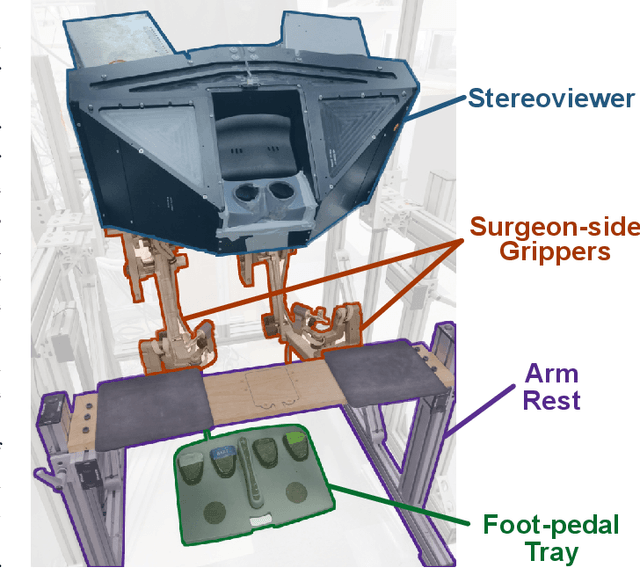
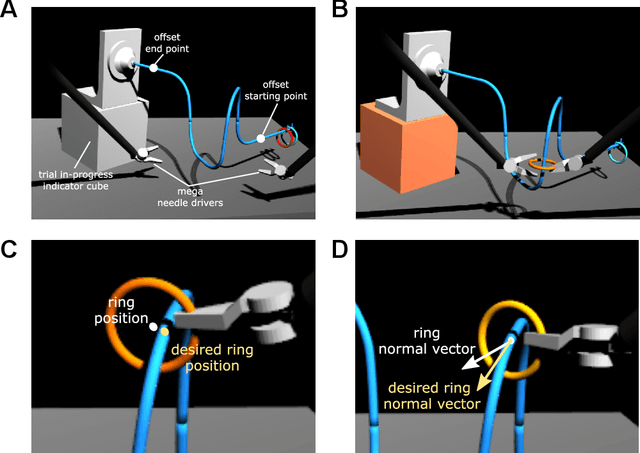
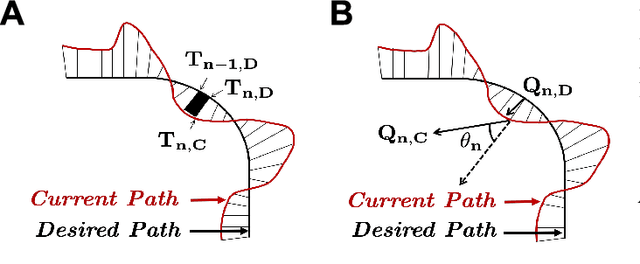
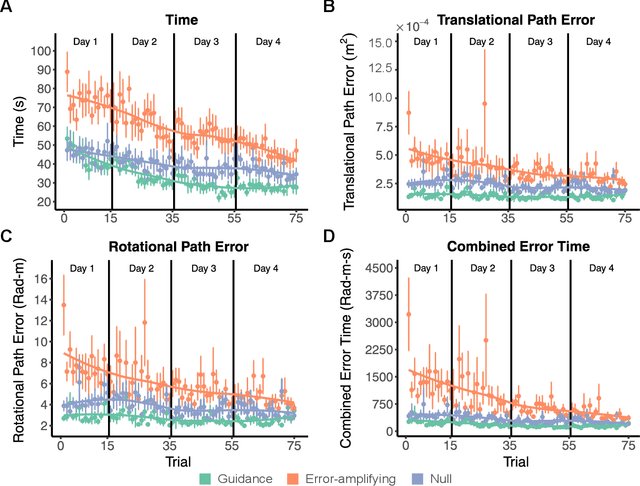
Teleoperated robotic systems have introduced more intuitive control for minimally invasive surgery, but the optimal method for training remains unknown. Recent motor learning studies have demonstrated that exaggeration of errors helps trainees learn to perform tasks with greater speed and accuracy. We hypothesized that training in a force field that pushes the operator away from a desired path would improve their performance on a virtual reality ring-on-wire task. Forty surgical novices trained under a no-force, guidance, or error-amplifying force field over five days. Completion time, translational and rotational path error, and combined error-time were evaluated under no force field on the final day. The groups significantly differed in combined error-time, with the guidance group performing the worst. Error-amplifying field participants showed the most improvement and did not plateau in their performance during training, suggesting that learning was still ongoing. Guidance field participants had the worst performance on the final day, confirming the guidance hypothesis. Participants with high initial path error benefited more from guidance. Participants with high initial combined error-time benefited more from guidance and error-amplifying force field training. Our results suggest that error-amplifying and error-reducing haptic training for robot-assisted telesurgery benefits trainees of different abilities differently.
A Modular 3-Degree-of-Freedom Force Sensor for Robot-assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery Research
Nov 10, 2022Zonghe Chua, Allison M. Okamura
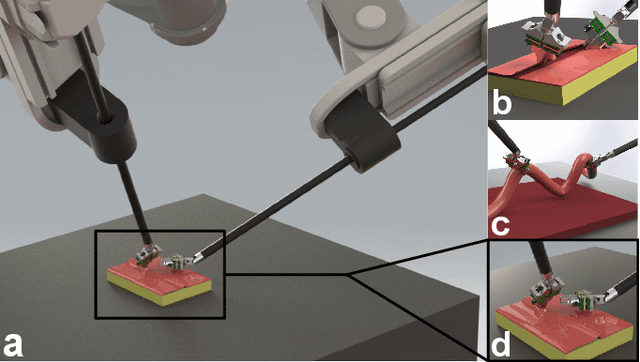
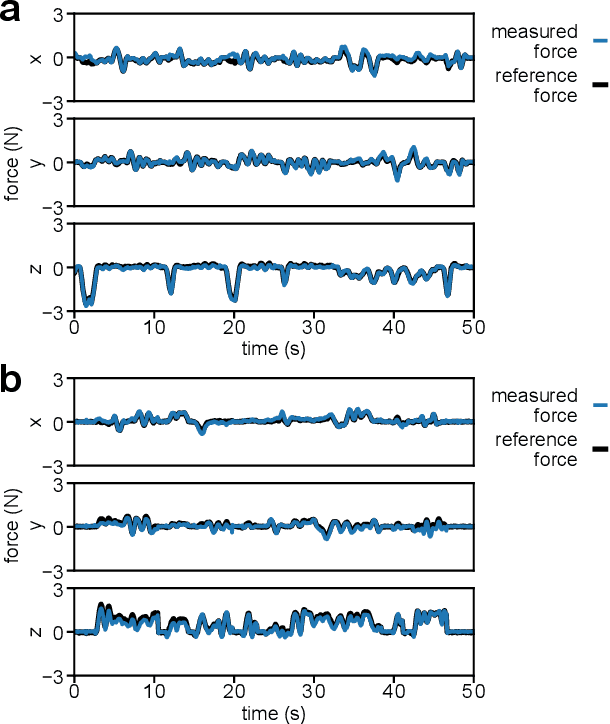
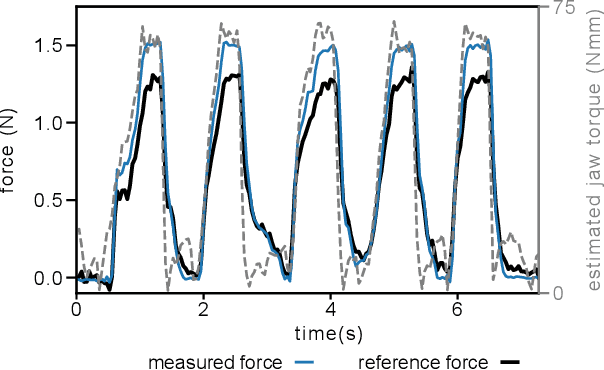
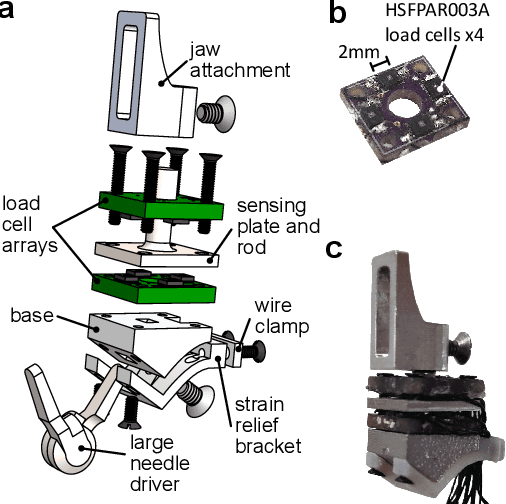
Effective force modulation during tissue manipulation is important for ensuring safe robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery (RMIS). Strict requirements for in-vivo distal force sensing have led to prior sensor designs that trade off ease of manufacture and integration against force measurement accuracy along the tool axis. These limitations have made collecting high-quality 3-degree-of-freedom (3-DoF) bimanual force data in RMIS inaccessible to researchers. We present a modular and manufacturable 3-DoF force sensor that integrates easily with an existing RMIS tool. We achieve this by relaxing biocompatibility and sterilizability requirements while utilizing commercial load cells and common electromechanical fabrication techniques. The sensor has a range of +-5 N axially and +-3 N laterally with average root mean square errors(RMSEs) of below 0.15 N in all directions. During teleoperated mock tissue manipulation tasks, a pair of jaw-mounted sensors achieved average RMSEs of below 0.15 N in all directions. For grip force, it achieved an RMSE of 0.156 N. The sensor has sufficient accuracy within the range of forces found in delicate manipulation tasks, with potential use in bimanual haptic feedback and robotic force control. As an open-source design, the sensors can be adapted to suit additional robotic applications outside of RMIS.
A 4-DoF Parallel Origami Haptic Device for Normal, Shear, and Torsion Feedback
Sep 24, 2021Sophia R. Williams, Jacob M. Suchoski, Zonghe Chua, Allison M. Okamura
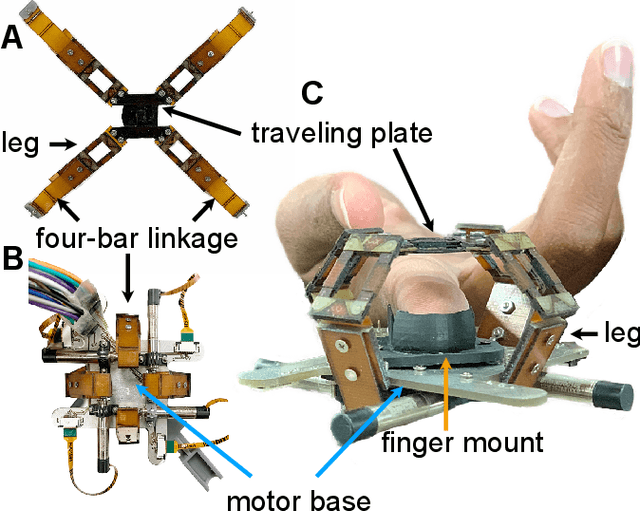
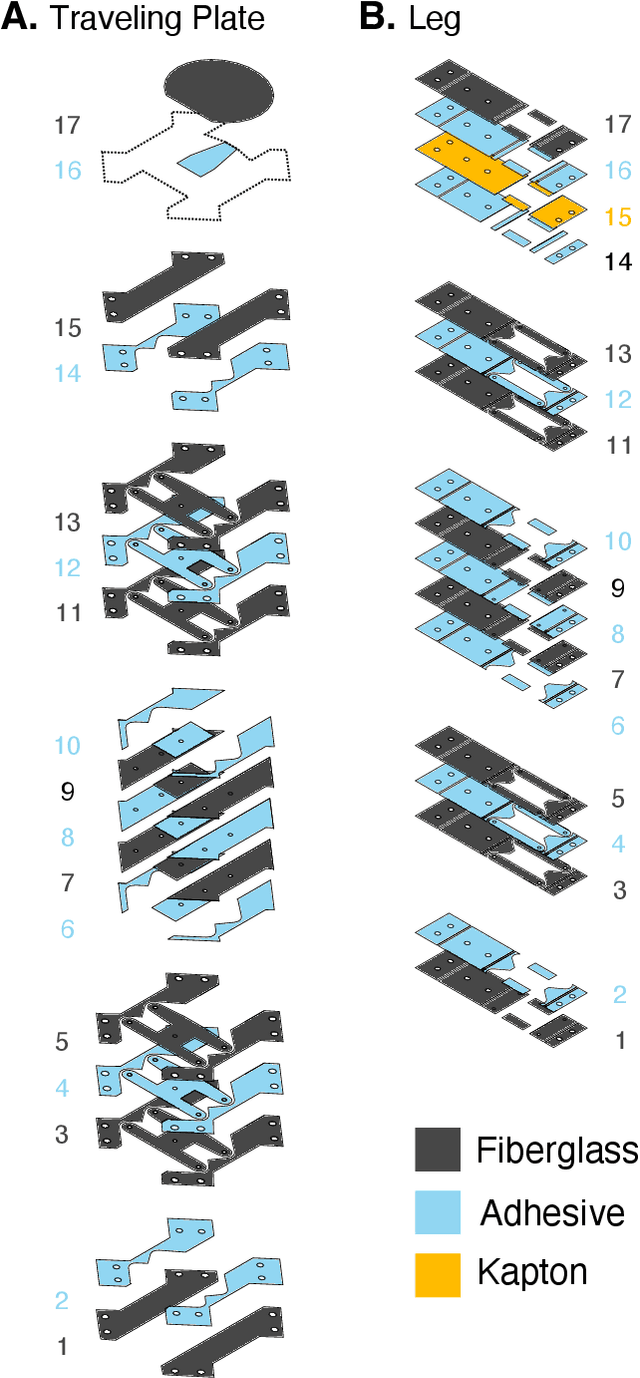
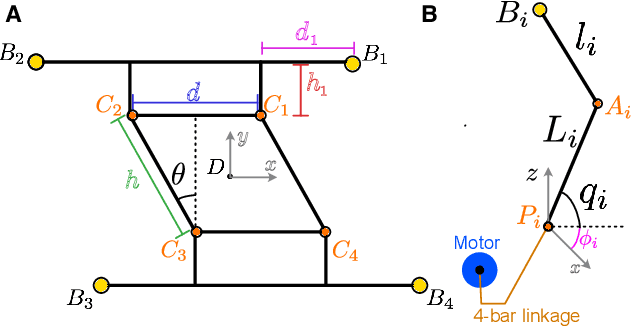
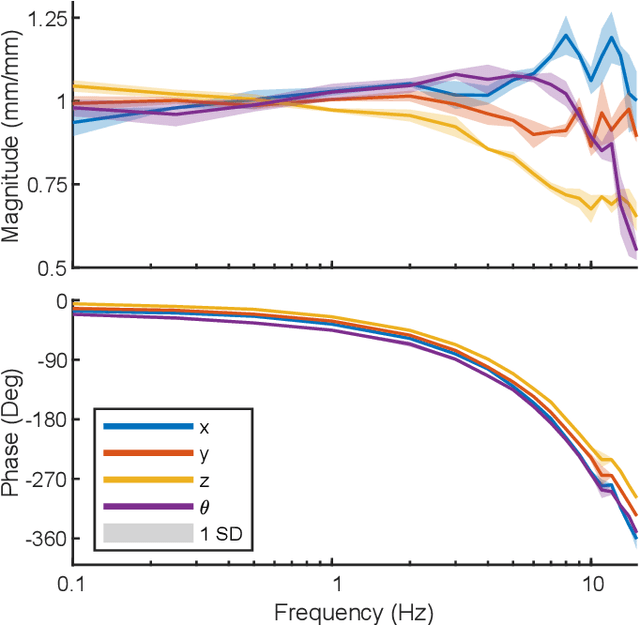
We present a mesoscale finger-mounted 4-degree-of-freedom (DoF) haptic device that is created using origami fabrication techniques. The 4-DoF device is a parallel kinematic mechanism capable of delivering normal, shear, and torsional haptic feedback to the fingertip. Traditional methods of robot fabrication are not well suited for designing small robotic devices because it is challenging and expensive to manufacture small, low-friction joints. Our device uses origami manufacturing principles to reduce complexity and the device footprint. We characterize the bandwidth, workspace, and force output of the device. The capabilities of the torsion-DoF are demonstrated in a virtual reality scenario. Our results show that the device can deliver haptic feedback in 4-DoFs with an effective operational workspace of 0.64cm$^3$ with $\pm 30 ^ \circ$ rotation at every location. The maximum forces and torques the device can apply in the x-, y-, z-, and $\theta$-directions, are $\pm$1.5N, $\pm$1.5N, 2N, and 5N$\cdot$mm, respectively, and the device has an operating bandwidth of 9Hz.
Robot-Assisted Surgical Training Over Several Days in a Virtual Surgical Environment with Divergent and Convergent Force Fields
Sep 23, 2021Yousi A. Oquendo, Zonghe Chua, Margaret M. Coad, Ilana Nisky, Anthony M. Jarc, Sherry M. Wren, Thomas S. Lendvay, Allison M. Okamura
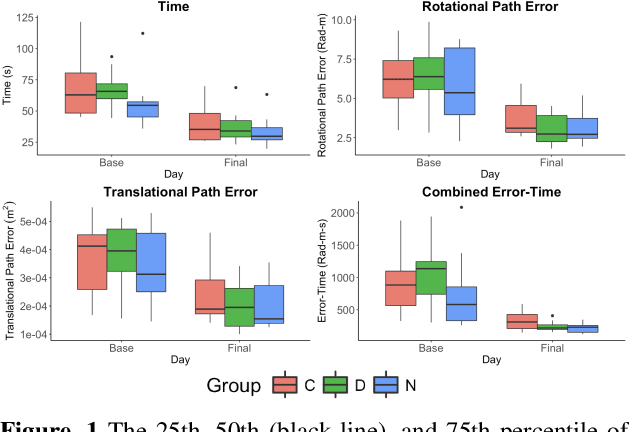
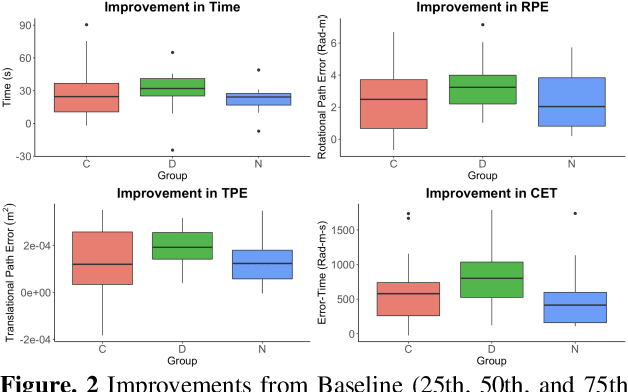
Surgical procedures require a high level of technical skill to ensure efficiency and patient safety. Due to the direct effect of surgeon skill on patient outcomes, the development of cost-effective and realistic training methods is imperative to accelerate skill acquisition. Teleoperated robotic devices allow for intuitive ergonomic control, but the learning curve for these systems remains steep. Recent studies in motor learning have shown that visual or physical exaggeration of errors helps trainees to learn to perform tasks faster and more accurately. In this study, we extended the work from two previous studies to investigate the performance of subjects in different force field training conditions, including convergent (assistive), divergent (resistive), and no force field (null).
* 2 pages, 2 figures, Hamlyn Symposium on Medical Robotics 2019
Characterization of Real-time Haptic Feedback from Multimodal Neural Network-based Force Estimates during Teleoperation
Sep 23, 2021Zonghe Chua, Allison M. Okamura

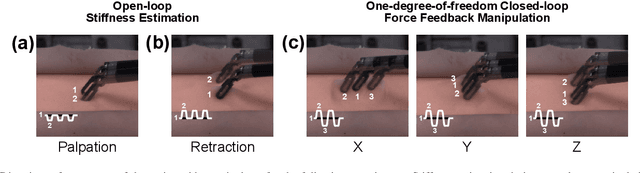
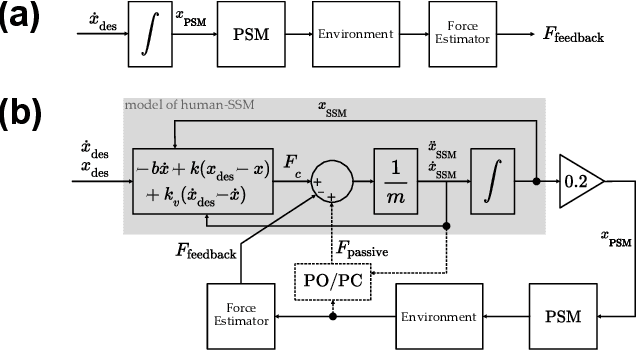

Force estimation using neural networks is a promising approach to enable haptic feedback in minimally invasive surgical robots without end-effector force sensors. Various network architectures have been proposed, but none have been tested in real-time with surgical-like manipulations. Thus, questions remain about the real-time transparency and stability of force feedback from neural network-based force estimates. We characterize the real-time impedance transparency and stability of force feedback rendered on a da Vinci Research Kit teleoperated surgical robot using neural networks with vision-only, state-only, or state and vision inputs. Networks were trained on an existing dataset of teleoperated manipulations without force feedback. We measured real-time transparency without rendered force feedback by commanding the patient-side robot to perform vertical retractions and palpations on artificial silicone tissue. To measure stability and transparency during teleoperation with force feedback to the operator, we modeled a one-degree-of-freedom human and surgeon-side manipulandum that moved the patient-side robot to perform manipulations. We found that the multimodal vision and state network displayed more transparent impedance than single-modality networks under no force feedback. State-based networks displayed instabilities during manipulation with force feedback. This instability was reduced in the multimodal network when refit with additional data collected during teleoperation with force feedback.
Toward Force Estimation in Robot-Assisted Surgery using Deep Learning with Vision and Robot State
Nov 13, 2020Zonghe Chua, Anthony M. Jarc, Allison M. Okamura
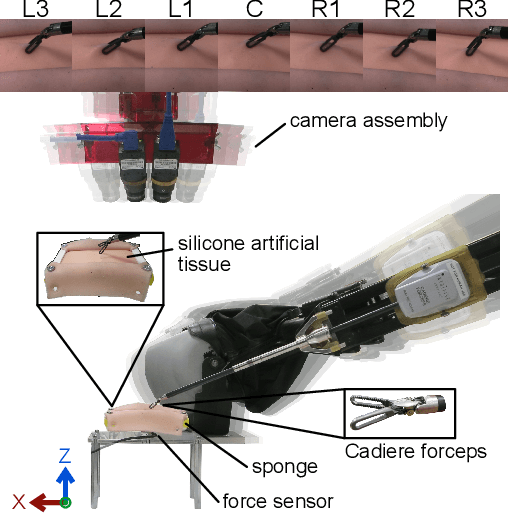
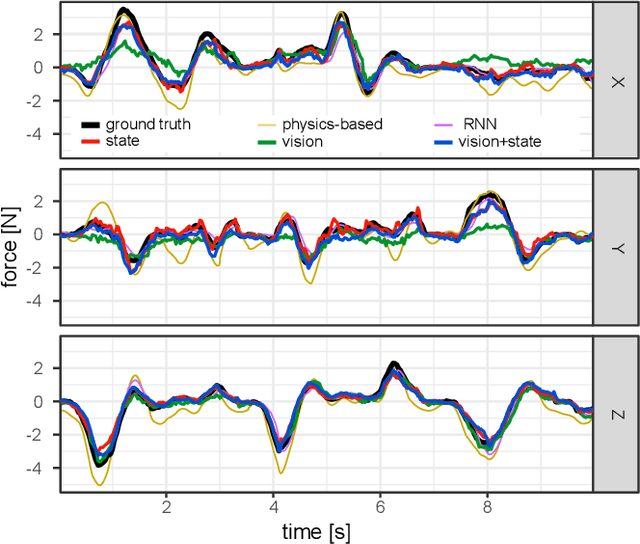
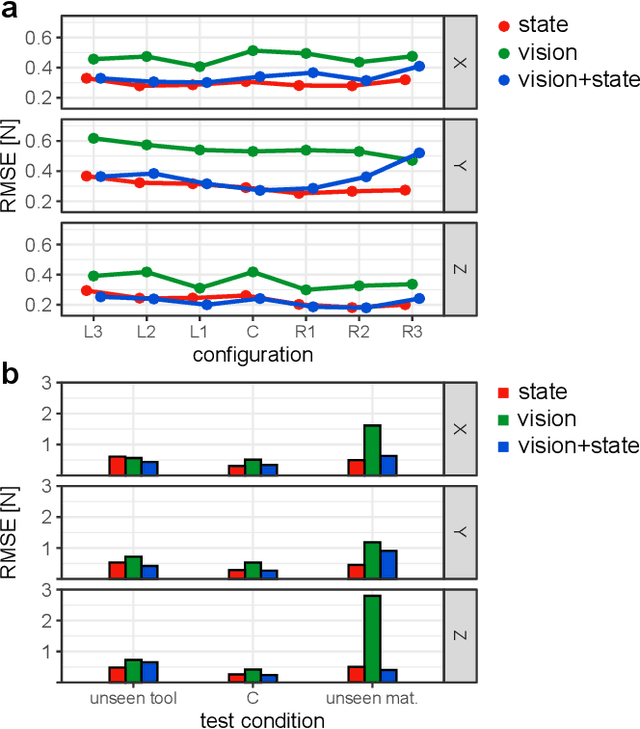
Knowledge of interaction forces during teleoperated robot-assisted surgery could be used to enable force feedback to human operators and evaluate tissue handling skill. However, direct force sensing at the end-effector is challenging because it requires biocompatible, sterilizable, and cost-effective sensors. Vision-based deep learning using convolutional neural networks is a promising approach for providing useful force estimates, though questions remain about generalization to new scenarios and real-time inference. We present a force estimation neural network that uses RGB images and robot state as inputs. Using a self-collected dataset, we compared the network to variants that included only a single input type, and evaluated how they generalized to new viewpoints, workspace positions, materials, and tools. We found that vision-based networks were sensitive to shifts in viewpoints, while state-only networks were robust to changes in workspace. The network with both state and vision inputs had the highest accuracy for an unseen tool, and was moderately robust to changes in viewpoints. Through feature removal studies, we found that using only position features produced better accuracy than using only force features as input. The network with both state and vision inputs outperformed a physics-based baseline model in accuracy. It showed comparable accuracy but faster computation times than a baseline recurrent neural network, making it better suited for real-time applications.
Evaluation of Non-Collocated Force Feedback Driven by Signal-Independent Noise
May 23, 2020Zonghe Chua, Allison M. Okamura, Darrel R. Deo
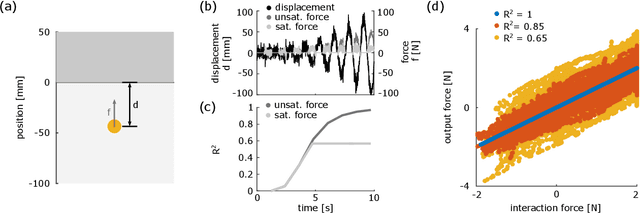
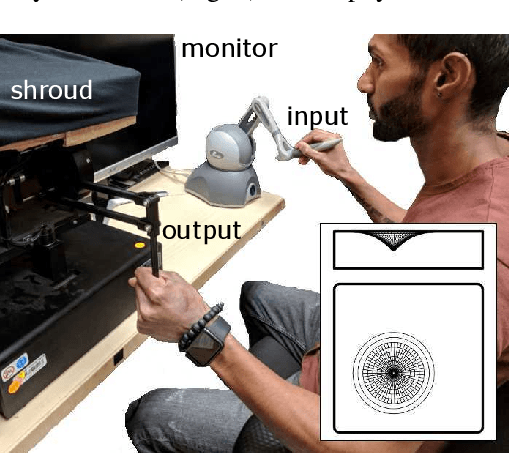
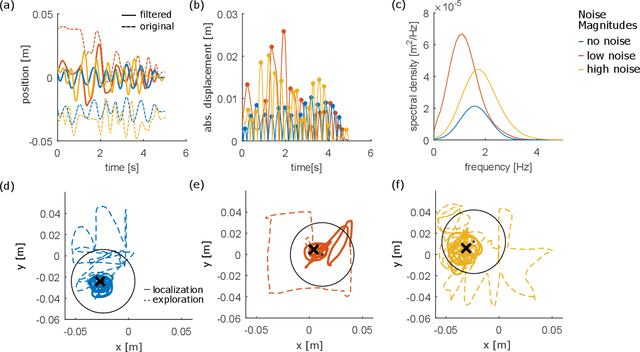
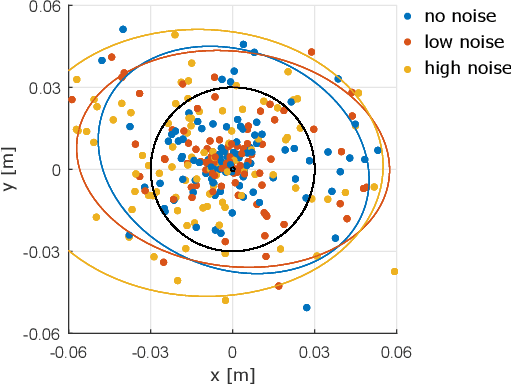
Individuals living with paralysis or amputation can operate robotic prostheses using input signals based on their intent or attempt to move. Because sensory function is lost or diminished in these individuals, haptic feedback must be non-collocated. The intracortical brain computer interface (iBCI) has enabled a variety of neural prostheses for people with paralysis. An important attribute of the iBCI is that its input signal contains signal-independent noise. To understand the effects of signal-independent noise on a system with non-collocated haptic feedback and inform iBCI-based prostheses control strategies, we conducted an experiment with a conventional haptic interface as a proxy for the iBCI. Able-bodied users were tasked with locating an indentation within a virtual environment using input from their right hand. Non-collocated haptic feedback of the interaction forces in the virtual environment was augmented with noise of three different magnitudes and simultaneously rendered on users' left hands. We found increases in distance error of the guess of the indentation location, mean time per trial, mean peak absolute displacement and speed of tool movements during localization for the highest noise level compared to the other two levels. The findings suggest that users have a threshold of disturbance rejection and that they attempt to increase their signal-to-noise ratio through their exploratory actions.
Task Dynamics of Prior Training Influence Visual Force Estimation Ability During Teleoperation of a Minimally Invasive Surgical Robot
Apr 28, 2020Zonghe Chua, Anthony M. Jarc, Sherry Wren, Ilana Nisky, Allison M. Okamura
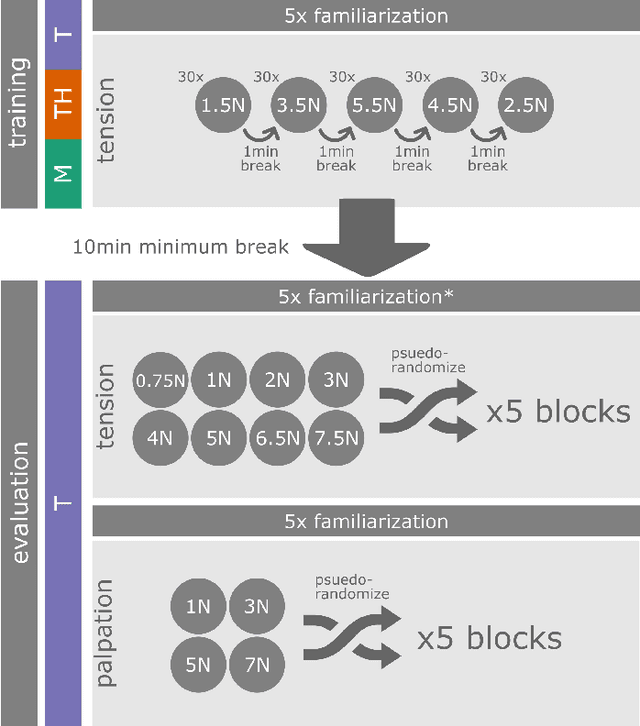
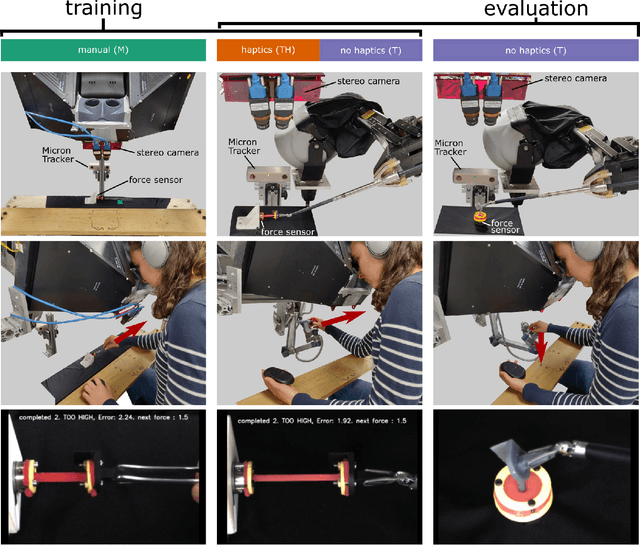
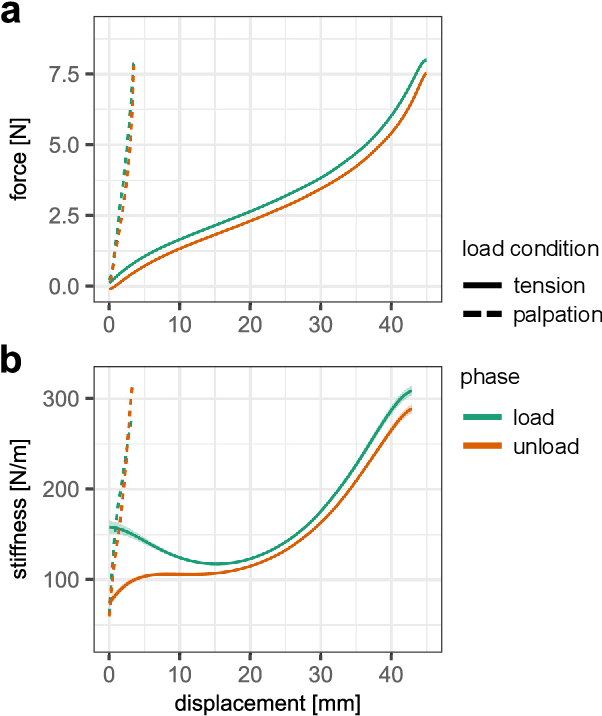
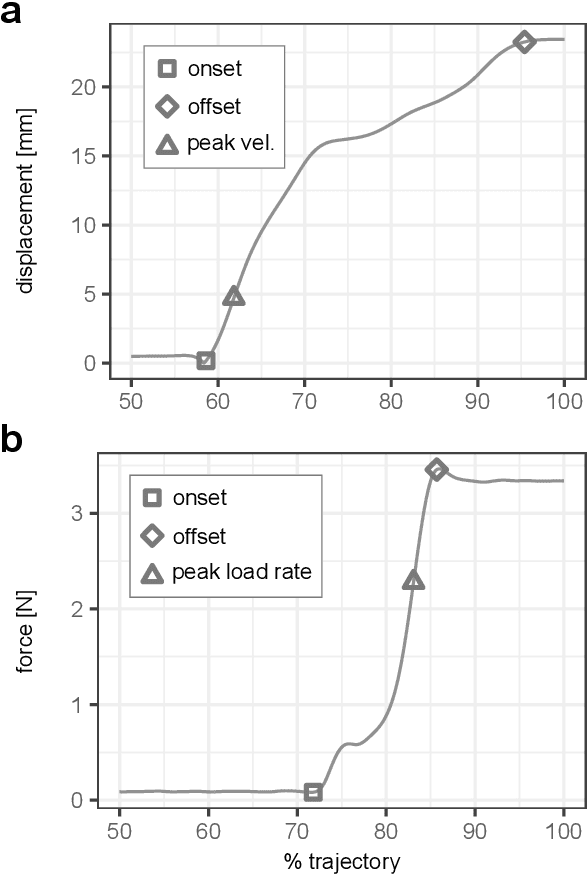
The lack of haptic feedback in Robot-assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery (RMIS) is a potential barrier to safe tissue handling during surgery. Bayesian modeling theory suggests that surgeons with experience in open or laparoscopic surgery can develop priors of tissue stiffness that translate to better force estimation abilities during RMIS compared to surgeons with no experience. To test if prior haptic experience leads to improved force estimation ability in teleoperation, 33 participants were assigned to one of three training conditions: manual manipulation, teleoperation with force feedback, or teleoperation without force feedback, and learned to tension a silicone sample to a set of force values. They were then asked to perform the tension task, and a previously unencountered palpation task, to a different set of force values under teleoperation without force feedback. Compared to the teleoperation groups, the manual group had higher force error in the tension task outside the range of forces they had trained on, but showed better speed-accuracy functions in the palpation task at low force levels. This suggests that the dynamics of the training modality affect force estimation ability during teleoperation, with the prior haptic experience accessible if formed under the same dynamics as the task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge